THP-1 Cells Unveiled: Pioneering Research in Leukemia
The THP-1 cell line, known as Tohoku Hospital Pediatrics-1, is a spontaneously immortalized culture of human monocytic leukemia cells. It serves as a versatile model in the study of monocyte biology, macrophage activities, and their roles in cancer and immunotherapy. The human leukemia THP1 cell line mirrors the physiological and functional properties of peripheral blood monocytes, making it an invaluable resource for investigating monocyte differentiation antigens and the broader aspects of monocyte physiology. This article provides a fundamental overview of the THP1 cell line.
General Information and Origin of the THP-1 Cell Line
For those new to working with the THP-1 cell line, understanding its basic characteristics is essential. We will discuss its definition, origin, morphology, size, and genomic properties.
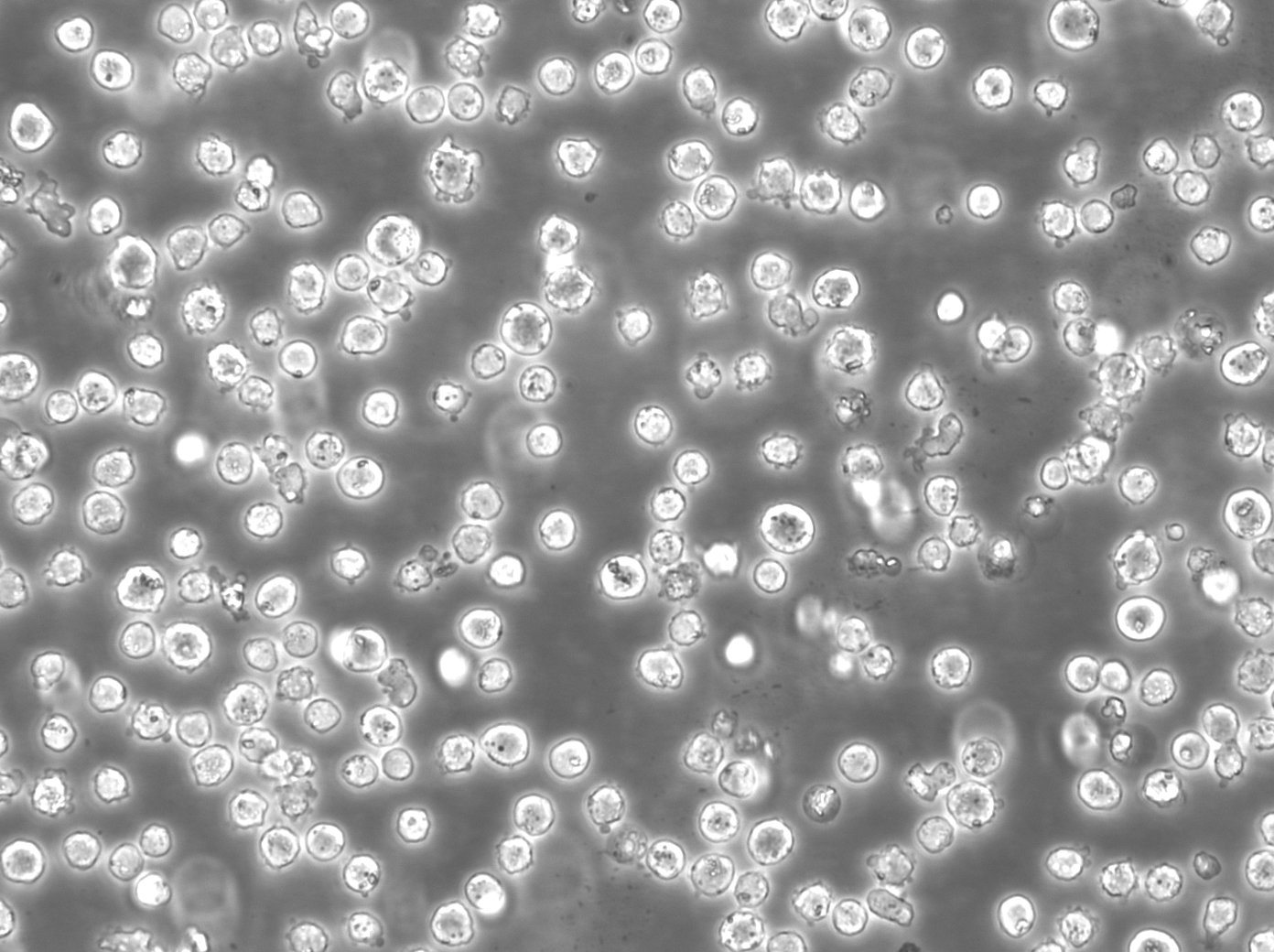
THP-1 Cell Line: THP-1 is a human monocytic leukemia cell line derived from the peripheral blood of a 1-year-old patient diagnosed with acute monocytic leukemia (M5 subtype) in 1980.
Morphology: THP-1 cells exhibit a round, large, and singular cell morphology.
Cell Size: These cells are relatively large, with a mean diameter exceeding 21 µm.
Genome and Ploidy: THP-1 is a near-diploid cell line, with karyotype analysis revealing a diploid chromosome number (n = 46).
Culturing the human leukemia cell line THP-1
Adequate knowledge of a cell line's characteristics simplifies its culturing process. This section provides crucial details for the culture and maintenance of the THP-1 cell line, including doubling time, culture media, adherence properties, seeding density, growth conditions, storage, and the processes of freezing and thawing.
Doubling Time: The doubling time of THP-1 cells is approximately 35 hours, although this can vary from 19 to 50 hours depending on the culture conditions.
Adherence: THP-1 cells grow in suspension but can differentiate into adherent macrophage-like cells under certain conditions.
Seeding Density: The ideal seeding density ranges from 1.0x10^5 to 1.5x10^6 viable cells/mL. This is achieved by diluting cells from a grown culture to the desired density.
Growth Medium: The recommended medium is RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 2.5 mM L-glutamine.
Growth Conditions: Cells should be cultured in a humidified incubator with a 5% CO2 supply at 37°C.
Storage: For long-term preservation, cells should be stored below -150°C to maintain viability.
Freezing Process: Use CM-1 or CM-ACF media for a slow freezing method, with a 1°C decrease in temperature per minute.
Thawing Process: Rapidly agitate for 40–60 seconds in a 37°C water bath containing an antimicrobial agent, then transfer to flasks with growth media.
Biosafety Level: THP-1 cells should be handled in biosafety level-1 laboratories.
This streamlined and scientifically precise description provides essential information on the THP-1 cell line, aiding researchers in their work with this valuable research tool.
Exploring Macrophage Biology with the THP-1 Cell Line: Insights into Differentiation, Function, and Immune Dynamics
THP-1 Cells as a Model for Macrophage Differentiation and Function Analysis
In relation to THP-1 cells, macrophage differentiation and functions take on a unique significance. THP-1 cells are a human leukemia monocyte line commonly used as a model to study monocyte and macrophage biology in vitro. They have the capacity to differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), mimicking the transition that peripheral monocytes undergo to become macrophages in the body. Upon differentiation, THP-1-derived macrophages can be polarized into either M1 or M2 macrophages through specific stimuli, reflecting the M1-associated pro-inflammatory or the M2-associated anti-inflammatory and tissue repair states.
These differentiated THP-1 macrophages retain key functions such as phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and cytokine production, making them an invaluable in vitro system for investigating the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying macrophage responses to various signals. Studies using THP-1 cells have provided insights into macrophage activities, including responses to infectious agents, interactions with cancer cells, and the role of macrophages in immunoregulation and inflammation. THP-1 cells also serve as a powerful tool for screening potential therapeutic compounds that can modulate macrophage activity and for exploring the immunological aspects of macrophage involvement in disease pathogenesis and resolution.
Exploring Macrophage Polarization and Activities with THP-1
THP-1 cells are instrumental in the study of human macrophage polarization, a process crucial for understanding immune responses in health and disease. By differentiating THP-1 cells into M0, M1, and M2 macrophages, researchers can examine classical macrophage activation (M1) associated with pro-inflammatory responses and M2 macrophage polarization, which is linked to anti-inflammatory or healing processes. This model of macrophage polarization allows for a deeper understanding of macrophages' display functions in various contexts, including tumor development and the response of cancer cells to therapies.
THP-1 in Cancer Research: From Apoptosis to Chemoresistance
The THP-1 cell line is a key player in studying cancer cell apoptosis and the mechanisms underlying tumor cell responses to treatments. Assays utilizing THP-1 cells, such as ADCP assays targeting specific cancer cells, help elucidate the interactions between macrophages and tumor cells, including HepG2 cells. Moreover, investigating caspase activity in THP-1 cells contributes to our comprehension of apoptosis, a critical process in cancer progression and treatment. The impact of chemotherapeutic agents, like etoposide, on THP-1 cells offers insights into the role of these cells in chemoresistance, further emphasizing their relevance in cancer research.
THP-1 Cells and Immunotherapy: Targeting and Response
In the realm of immunotherapy, THP-1 cells are used to model the interaction between immune cells and cancer, investigating how macrophages can be harnessed to target cancer cells, such as Raji cells. The study of mRNA and protein expression in THP-1 cells aids in understanding the intricate signaling pathways involved in the immune response and the potential for therapeutic intervention. This research is pivotal for developing strategies to manipulate macrophage activities towards enhanced immunotherapeutic outcomes.
The THP-1 cell line, through its ability to mimic peripheral monocytes and undergo macrophage polarization, has become a cornerstone in the study of human leukemia, macrophage biology, and their implications in cancer and immunotherapy. Its versatility and relevance in various assays make it an essential tool for advancing our understanding of the immune system's role in health and disease.
Explore Our THP-1 Cell Line Collection
Research Applications of THP-1 Cells
Before working with any cell line, you go through its research application and understand how to utilize these cells in your study. Here we have mentioned a few prominent research applications of the THP-1 cell line.
The THP-1 cell line is widely used in immunology research because it can differentiate into various immune cells. Here are some examples of studies that have utilized THP-1 cells:
- A 2018 study used THP-1 cells to derive macrophage cells and investigate inflammatory pathways and related mechanisms. The researchers found that a protein called apolipoprotein A-1 binding protein (AIBP) could halt inflammatory pathways by binding to apoA-1 and stabilizing ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) [3].
- Another study used THP-1 cells to develop monocyte-like cells and investigate the effects of the neuroprotectant docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on these cells in the context of Alzheimer's disease. The study explored potential mechanisms underlying the interaction of the amyloid beta (Aβ) protein [4].
- THP-1 cell line-derived macrophages were utilized in another study to investigate the tumor-promoting potential of exosomes secreted by pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells [5].
Publications Highlighting THP-1 Cells in Scientific Research
There are a multitude of studies on THP-1 cells. Here, we have listed a few relevant examples:
- Apolipoprotein A-1 binding protein inhibits inflammatory signaling pathways by binding to apolipoprotein A-1 in THP-1 macrophages. This study was published in the Circulation Journal in 2018. This research treated THP-1 cell line-derived macrophages with lipopolysaccharide to induce inflammatory pathways. The study proposed that Apolipoprotein A-1 binding protein prevents inflammatory cascades by binding to Apolipoprotein A-1 protein.
- DHA attenuates Aβ-induced necroptosis through the RIPK1/RIPK3 signaling pathway in THP-1 monocytes. This research proposed that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibits necroptosis induced by amyloid beta protein in THP-1-derived monocytes in the context of Alzheimer's disease
- Tumor-promoting effects of pancreatic cancer cell exosomes on THP-1-derived macrophages: In this publication, Linton and colleagues observed the cancer-promoting effect of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell-secreted exosomes on THP-1 cell line-originated macrophages.
- The effects of waste sorting in environmental microbiome, THP-1 cell viability and inflammatory responses: This study utilized macrophages derived from the THP-1 cell line and studied the effect of the microbiome present in the waste sorting industry on the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by these cells.
- Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M (IFNγ+ LPS), M (IL-4) and M (IL-10) phenotypes: This study described protocols for inducing differentiation in THP-1 cells and developing macrophages with particular phenotypes.
- Pro-atherogenic proteoglycanase ADAMTS-1 is down-regulated by lauric acid through PI3K and JNK signaling pathways in THP-1 derived macrophages. This paper was published in Molecular Biology Reports in 2019. This study explored the therapeutic potential of lauric acid on THP-1-derived macrophages. The results showed that lauric acid stabilizes atherosclerosis plaque and inhibits thrombosis by modulating ADAMS-1 (pro-atherogenic proteoglycanase) expression.
Resources for the THP-1 Cell Line
This section will cover all the available online resources on THP-1 cells. This will significantly help you learn culturing, differentiation, and transfection protocols.
Cell culture protocols
These are a few resources explaining culturing and handling protocols for THP-1 cells.
- Culturing and differentiation protocol: This document contains detailed and comprehensive information about cell culture media, subculturing, freezing and thawing, and differentiation protocols of these cells.
- Subculturing THP-1 cells: This document comprises a subculturing protocol for THP-1 cells.
Transfection protocols
- Transfection of THP-1 cells: This link is about transfecting THP-1 cells with plasmid DNA.
- This document describes a transfection protocol of THP-1 cells.
Videos related to THP-1 cells
THP-1 is a widely cultured cell line. Many video resources are available explaining the handling and culturing of this cell line:
- Culture THP-1 cells: This video is about THP-1 cell line culturing.
- Transfection of THP-1 cell line: This video shows a protocol for highly efficient transfection of THP-1 cells.
We hope this article contains appropriate information about THP-1 cell culturing, differentiation, advantages, and research applications. If you plan to use this in vitro cell model of acute myeloid leukemia in your research, consider ordering from us.
FAQs for the THP-1 cell line
THP-1 cells are a human monocytic cell line derived from an acute monocytic leukemia patient. They are extensively used in research to study monocyte/macrophage functions, mechanisms of immunity and inflammation, and monocytic leukemia.
THP-1 macrophages are differentiated forms of THP-1 monocytes. When treated with certain agents like Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), THP-1 cells differentiate into macrophages, making them useful models for studying macrophage biology and function.
In research, THP-1 cells are used to study various aspects of monocyte/macrophage biology, including differentiation, activation, response to infections, and the role of macrophages in disease processes, such as cancer and inflammation.
References
- Chanput, W., J.J. Mes, and H.J. Wichers, THP-1 cell line: an in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. International immunopharmacology, 2014. 23(1): p. 37-45.
- Chanput, W., V. Peters, and H. Wichers, THP-1 and U937 Cells. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: in vitro and ex vivo models, 2015: p. 147-159.
- Zhang, M., et al., Apolipoprotein A-1 binding protein inhibits inflammatory signaling pathways by binding to apolipoprotein A-1 in THP-1 macrophages. Circulation Journal, 2018. 82(5): p. 1396-1404.
- Yuan, S., et al., DHA attenuates Aβ-induced necroptosis through the RIPK1/RIPK3 signaling pathway in THP-1 monocytes. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2020. 126: p. 110102.
- Linton, S.S., et al., Tumor-promoting effects of pancreatic cancer cell exosomes on THP-1-derived macrophages. PLoS One, 2018. 13(11): p. e0206759.