RAW 264.7 Cell Line in Macrophage and Immunology Research
The RAW 264.7 cell line serves as a robust in vitro model for murine macrophages, fundamental to the realm of immunological research. Originating from a male BALB/c mouse, these cells were transformed by the Abelson murine leukemia virus, resulting in a macrophage-like cell line. Due to their functional stability and inherent ability to perform both phagocytosis and pinocytosis, RAW 264.7 cells are essential for the study of host-pathogen interactions, making them a cornerstone in immunological research endeavors [1,2].
Morphological Characteristics and Growth Behavior
Upon examination, RAW 264.7 cells exhibit semi-adherent growth with a propensity to form both spindle-shaped adherent cells and spherical floating viable cells, with a cellular diameter ranging from 10 to 20 µm. This polymorphic nature and adaptability in culture conditions make RAW 264.7 cells a versatile tool for experimental manipulation and observation.
Immunological Function and Antigen Presentation
As antigen-presenting cells, RAW 264.7 cells play a critical role in the immune system. Their function extends beyond simple pathogen recognition to the processing and presentation of antigens to T cells, thereby orchestrating a comprehensive immune response. This dynamic facilitates a deeper understanding of how the immune system identifies and neutralizes foreign entities.
Macrophage Polarization: The M0, M1, and M2 Paradigm
RAW 264.7 cells, in their basal state as M0 macrophages, possess the remarkable capacity to polarize into either the M1 pro-inflammatory or the M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype. This polarization capability provides researchers with a model to study the influences and effects of various cytokines and environmental factors on macrophage function and immune responses [3,4].
Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Remodeling
Although not osteoclasts themselves, RAW 264.7 cells have been instrumental in studying osteoclastogenesis—the process of osteoclast formation. These cells facilitate the exploration of osteoclastic gene expression and their responsiveness to receptor activation. This research has profound implications for understanding the pathophysiology of conditions such as osteoporosis, where dysregulated bone remodeling is a hallmark.
Cell culture information on RAW 264.7
Before you start your experiments, you must understand some basic information about this powerful cell line. Do you know the doubling time of RAW 264.7 cells? What's the seeding density for these cells, and are they adherent? Moreover, what are the optimal growth conditions for RAW 264.7? Keep reading to uncover all the answers you need to work with this incredible cell line!
|
Cell Culture Information |
RAW 264.7 Cell Line |
|
Population-doubling time |
11 to 30 hours |
|
Adherent or in suspension |
Mostly adherent, with some suspension cell populations |
|
Seeding density |
4 x 10^4 cells/cm^2 |
|
Recommended growth medium |
RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and L-glutamine (2.5 mM) |
|
Optimal growth conditions |
Humidified incubator with 5% CO2 and 37°C temperature |
|
Media replacement |
2 to 3 times a week |
|
Storage |
Vapor phase of liquid nitrogen |
|
Freezing medium |
CM-1 or CM-ACF |
|
Freezing process |
Slow freezing |
|
Thawing process |
Rapid agitation in 37°C water bath |
|
Biosafety level |
BSL-2 laboratory recommended |
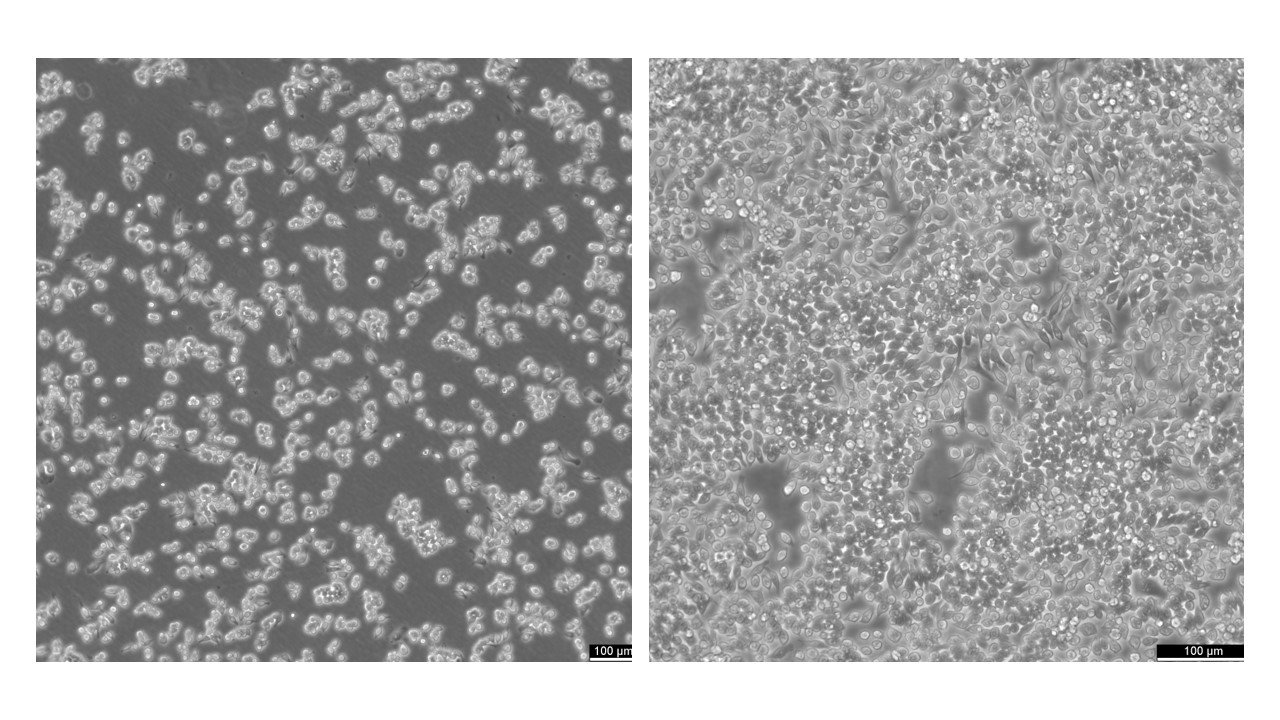
Murine RAW 264.7 macrophages at different confluencies.
Advantages and disadvantages of RAW 264.7 cells
Advantages
- Easy culturing: The RAW 264.7 cell line is easy to grow and maintain in the laboratory without any complicated requirements.
- Well-characterized: RAW 264.7 is a well-characterized cell line, which means it has stable phenotypic and functional features.
- In vitro model of macrophages: As RAW 264.7 cells are macrophages, they exhibit essential macrophage-like functions such as phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Thus, they are often used as an in vitro model of macrophages.
- Differentiation to osteoclasts: RAW 264.7 cells can be differentiated into osteoclasts using specific molecular factors. These differentiated cells are capable of performing bone remodeling, similar to osteoclasts.
Disadvantages
- Poor representation of primary macrophages: As a transformed cell line, RAW 264.7 may not accurately represent the features of primary macrophages and may have some differences in gene expression, phenotype, and function.
- Limitations in drug screening: RAW 264.7 cells may not be suitable for all types of drug screening assays, and their responses to some drugs may differ from primary macrophages.
- Strong cell adhesion: RAW 264.7 cells strongly adhere to the surface of the culture flask and can sometimes be tricky to detach.
Applications of RAW 264.7 Cells in Macrophage Mimicry and Immunological Studies
Modeling Cellular Immunological Responses
The RAW 264.7 cell line, reflecting the functionalities of authentic macrophages, is a key model for the investigation of cell responses to pathogens and immunological stimuli. A study highlighting this aspect assessed the immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects of heat-killed lactic acid bacteria on these cells, providing significant findings in immune system regulation [5].
Complementing this, research conducted in 2019 elucidated the immunological impact of RAW 264.7 exposure to polysaccharides from the plant Polygonatum sibiricum. The study concluded that these compounds trigger an immune response by the activation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways, offering deep molecular understanding [6].
Exploration of Osteoclastogenesis
Functioning as a surrogate for osteoclast differentiation studies, RAW 264.7 cells contribute to the elucidation of osteoclast behavior and differentiation pathways. Such research expands our knowledge on bone resorption mechanisms and osteoporosis pathogenesis. Advanced imaging techniques are often utilized to monitor intracellular changes and analyze heme metabolism within these cells.
Gaining Molecular Insights into Osteoclastogenesis
Despite their primary role as a macrophage model, RAW 264.7 cells are also employed for in vitro osteoclastogenesis research. By inducing osteoclast-like characteristics in these cells, researchers gain insight into the differentiation process and pre-osteoclast behavior, although it is crucial to consider the cell line’s inherent characteristics and origin in these studies.
Natural Product Bioactivity Screening
Screening for bioactivity in natural products is another application where RAW 264.7 cells excel. For example, their use in a Korean study investigating the immunostimulatory properties of a herbal mixture showcased the cell line's effectiveness in identifying bioactive compounds in natural substances [7].
Pioneer your research with our RAW 264.7 cells
Research publications using RAW 264.7 cells
Many research publications are available on mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7:
- Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum Delar. ex Redoute induce an immune response in the RAW264. 7 cell line via an NF-κB/MAPK pathway: This study proposed that polysaccharides obtained from the Polygonatum sibiricum plant can trigger an immune response in the mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 via regulating NF-κB/MAPK signaling cascade.
- Immunomodulatory effects of Tinospora crispa extract and its major compounds on the immune functions of RAW 264.7 macrophages: This article published in the International Immunopharmacology journal describes thatTinospora crispa plant extract and its major constituents have an immunomodulatory and immune-stimulatory effect on the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line.
- Heat-killed lactic acid bacteria inhibit nitric oxide production via inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in RAW 264.7 cells: This study proposed that heat-killed lactic acid bacteria can potentially be used in probiotic product synthesis because they possess immune-modulatory and antioxidant properties. Researchers used RAW 264.7 cells to study these biological activities.
- Effect of herbal formulation on immune response enhancement in RAW 264.7 macrophages: This study used RAW 264.7 cells to study the immune-stimulatory effect of an herbal formulation named KM1608. The study suggested KM1608 as a potential immune response enhancement agent.
- A screening of plants used in Colombian traditional medicine revealed the anti-inflammatory potential of Physalis angulata calyces: This paper published in the Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences investigated the anti-inflammatory potential of 10 commonly used traditional Colombian plants using LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.
RAW 264.7 cells: Resources, Protocols, Videos & More
RAW 264.7 cells are often used in transfection studies. The following resources explain different transfection methods used for the RAW 264.7 cell line.
- Transfecting RAW 264.7 cells: This website will provide a protocol for transfecting RAW 264.7 macrophages using a lipofectamine reagent.
- Transfection protocol: This published article describes a detailed protocol for the transfection of RAW 264.7 cells.
- Efficient Transfection method for RAW 264.7 cells: This document describes another practical transfection approach using RAW 264.7 cells.
Videos related to RAW 264.7 cell line
- Culturing RAW 264.7 cells: This video explains RAW 264.7 cells passaging protocol.
- Transfection method: This video is about transfecting RAW 264.7 cells with a reporter gene.
Essential FAQs on the RAW 264.7 Cell Line: Insights into Macrophage Mimicry and Osteoclastogenesis Research
The RAW 264.7 cell line was derived from the ascites of a tumor induced by the Abelson murine leukemia virus (A-MuLV) in a male BALB/c mouse.
RAW 264.7 cells are used as a model for macrophages because of their ability to perform key functions such as phagocytosis and pinocytosis, which are indicative of innate immune responses.
Yes, while RAW 264.7 cells are not osteoclasts, they can be used to study the process of osteoclastogenesis and osteoclastogenic gene expression, which contributes to our understanding of bone health and diseases like osteoporosis.
RAW 264.7 cells respond to microbial stimuli by mimicking macrophage responses, making them ideal for studying host-pathogen interactions and the cellular responses to various biological systems.
Cytokine production in RAW 264.7 cells is crucial for understanding the inflammatory process and the cell signaling pathways involved in immune responses, such as the NF-κB/MAPK pathways.
No, RAW 264.7 cells are not primary cells; they are an immortalized cell line. Primary cells refer to cells taken directly from living tissue and have a limited lifespan in culture.
RAW 264.7 cells are cultured in specific media that support their growth and are maintained under controlled temperature and atmospheric conditions to ensure their functional stability for experimental use.
RAW 264.7 cells, in their basal state (M0), can be polarized to exhibit either M1-like pro-inflammatory or M2-like anti-inflammatory properties, depending on the stimuli they are exposed to in the culture.
Yes, RAW 264.7 cells are frequently used to assess the bioactivity of natural products, including plant-derived compounds, for their potential immunomodulatory or therapeutic effects.
Typical markers include F4/80 and CD11b, which are commonly used to confirm the macrophage-like phenotype of RAW 264.7 cells, alongside their functional markers such as resistant acid phosphatase and phagocytic activity.
References
- Taciak, B., et al., Evaluation of phenotypic and functional stability of RAW 264.7 cell line through serial passages. PloS one, 2018. 13(6): p. e0198943.
- Wang, S., et al., Inflammatory macrophages interrupt osteocyte maturation and mineralization via regulating the Notch signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine, 2022. 28(1): p. 102.
- Orekhov, A.N., et al., Monocyte differentiation and macrophage polarization. Vessel Plus, 2019. 3: p. 10.
- Khabipov, A., et al., RAW 264.7 macrophage polarization by pancreatic cancer cells–a model for studying tumour-promoting macrophages. Anticancer Research, 2019. 39(6): p. 2871-2882.
- Kang, C.-H., et al., Heat-killed lactic acid bacteria inhibit nitric oxide production via inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in RAW 264.7 cells. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2021. 13(6): p. 1530-1538.
- Zhang, J., et al., Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum Delar. ex Redoute induce an immune response in the RAW264. 7 cell line via an NF-κB/MAPK pathway. RSC advances, 2019. 9(31): p. 17988-17994.
- Trinh, T.A., et al., effect of herbal formulation on immune response enhancement in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biomolecules, 2020. 10(3): p. 424.

