RKO Cells












General information
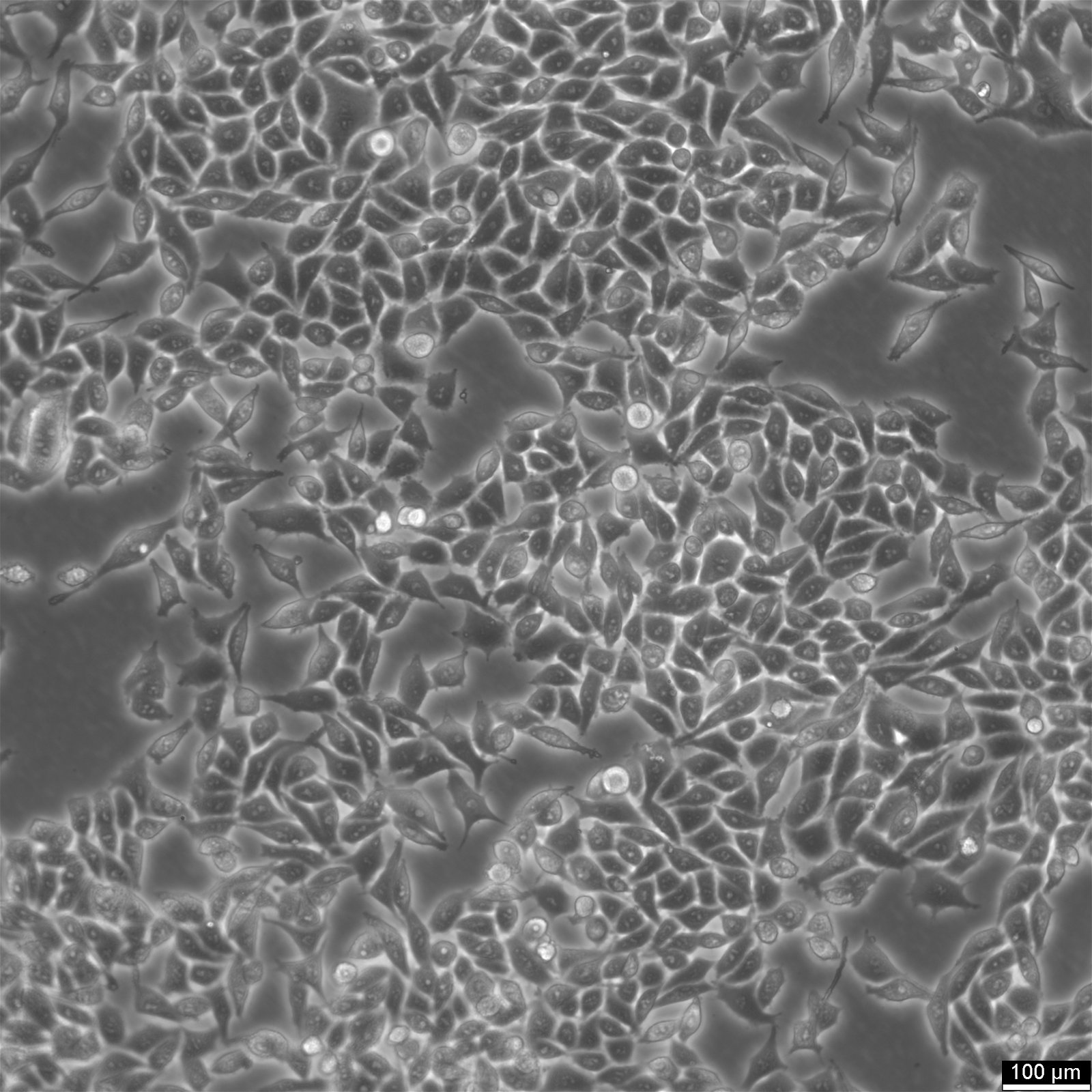
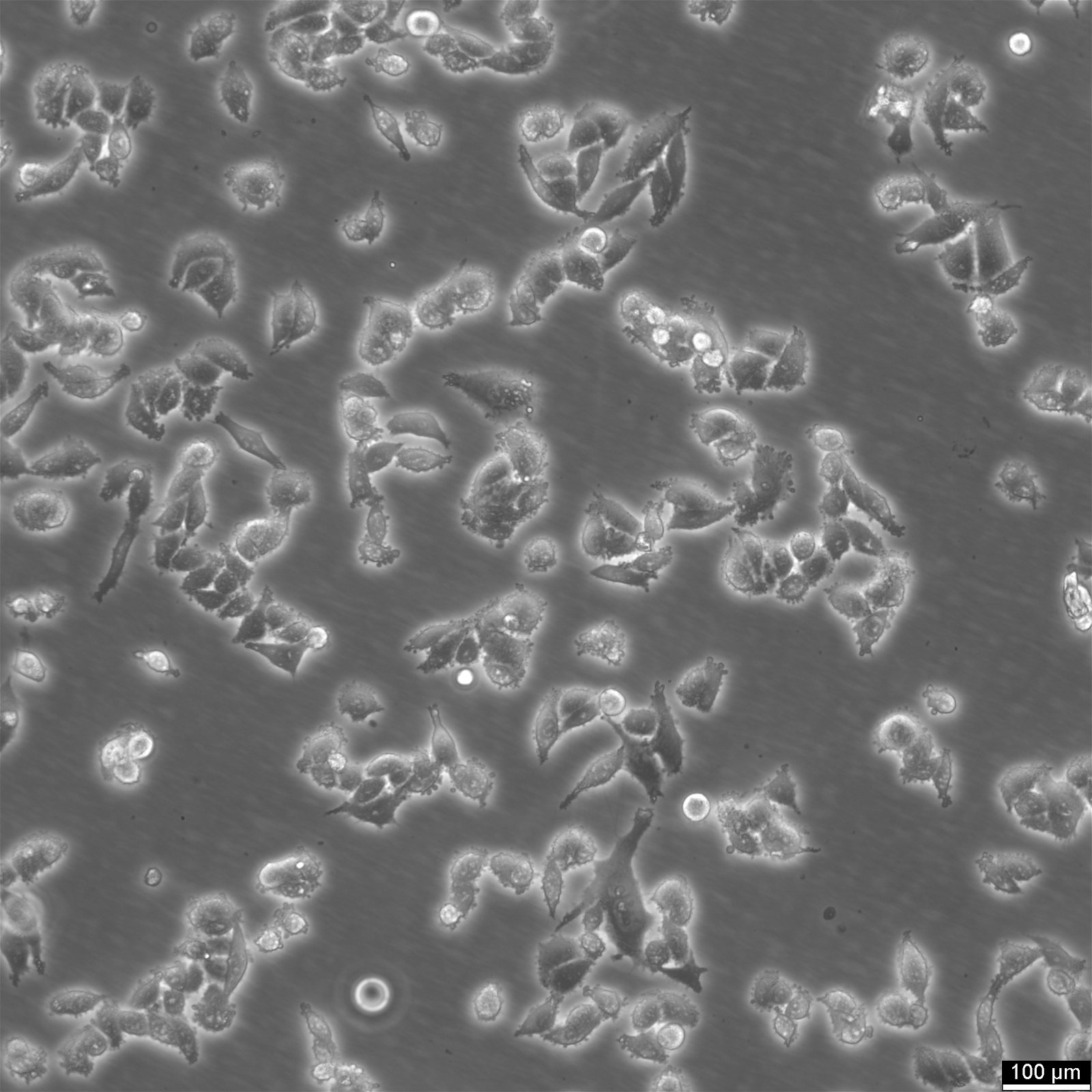
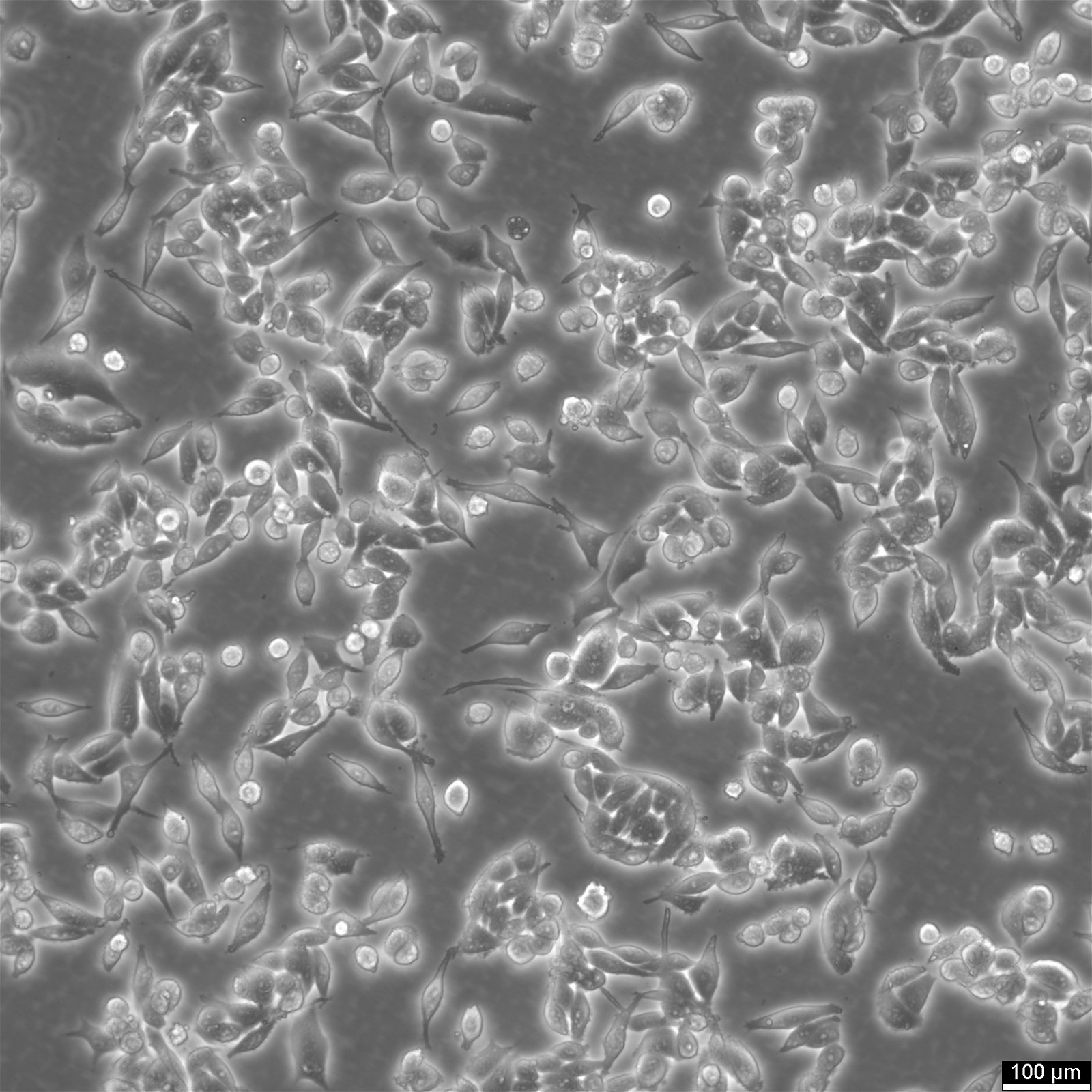
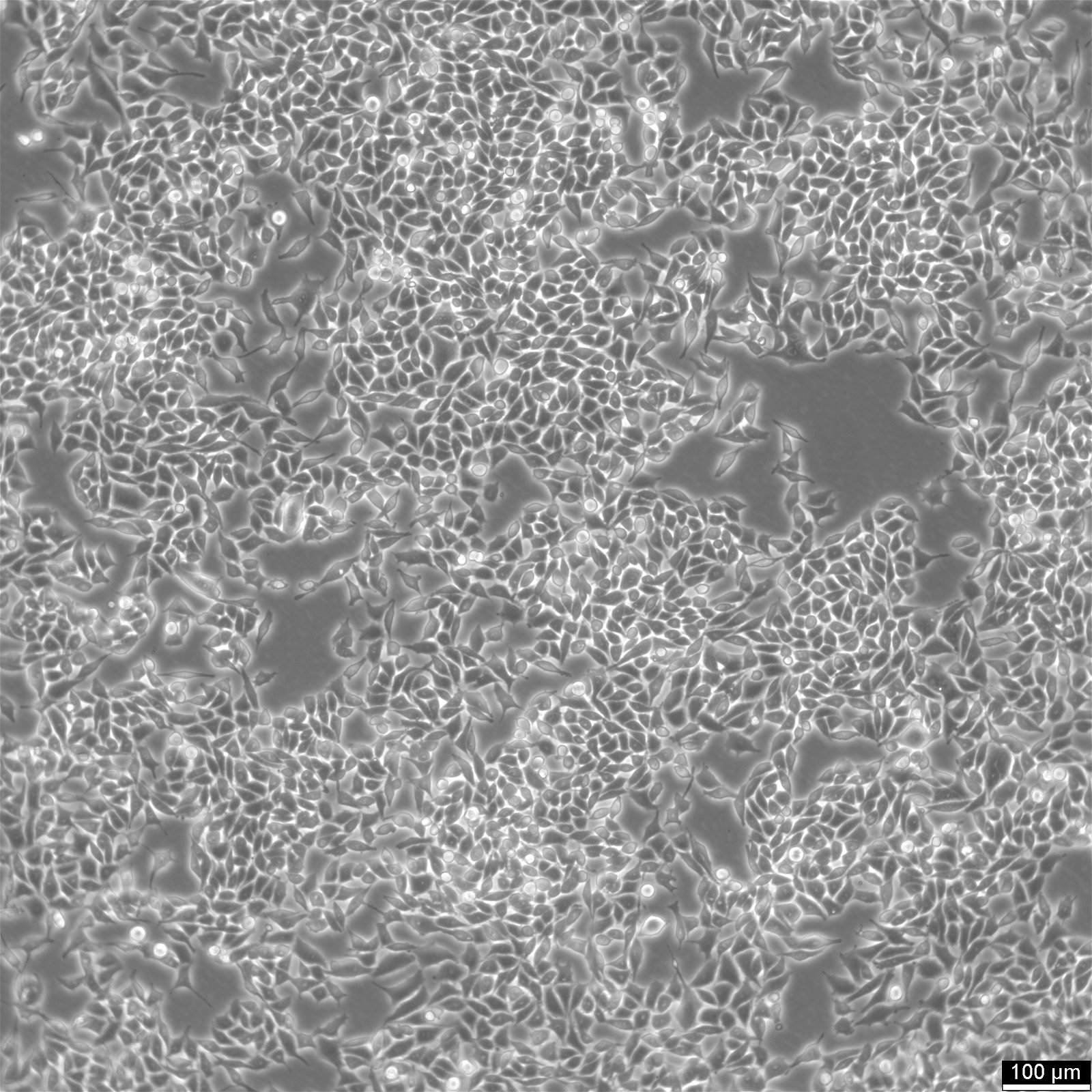
| Description | RKO cells are a human colorectal carcinoma cell line widely used in research related to colon cancer. They are derived from a moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the colon and are notable for their wild-type p53 status, which is uncommon among many cancer cell lines. This feature makes RKO cells particularly valuable for studying p53 functions and the cellular mechanisms of DNA repair and apoptosis in the context of colorectal cancer. RKO cells exhibit epithelial morphology and are characterized by their genetic stability and responsiveness to a variety of genetic and pharmacological manipulations. They are utilized in studies focusing on the molecular pathways involved in cancer progression, including cell cycle regulation, signal transduction, and metastasis. RKO cells provide insights into the role of various genes and environmental factors in colorectal cancer development and offer a platform for testing the efficacy of anti-cancer drugs. Additionally, RKO cells are used to explore the complex interactions between cancer cells and their microenvironment, as well as the immune response to tumor cells. Their sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents and radiation makes them suitable for use in drug discovery and development, helping to identify potential therapeutic targets and evaluate new treatment strategies for colorectal cancer. Overall, RKO cells are a fundamental resource in colorectal cancer research, contributing significantly to our understanding of the disease's molecular biology and aiding in the development of more effective treatments. |
|---|---|
| Organism | Human |
| Tissue | Colon |
| Disease | Colon carcinoma |
Characteristics
| Ethnicity | African |
|---|---|
| Morphology | Epithelial |
| Growth properties | Adherent |
Identifiers / Biosafety / Citation
| Citation | RKO (Cytion catalog number 305035) |
|---|---|
| Biosafety level | 1 |
Expression / Mutation
| Receptors expressed | Urokinase receptor(u-PAR) |
|---|---|
| Tumorigenic | Yes |
Handling
| Culture Medium | EMEM, w: 2 mM L-Glutamine, w: 1.5 g/L NaHCO3, w: EBSS, w: 1 mM Sodium pyruvate, w: NEAA (Cytion article number 820100c) |
|---|---|
| Medium supplements | Supplement the medium with 10% FBS |
| Passaging solution | Accutase |
| Subculturing | Remove the old medium from the adherent cells and wash them with PBS that lacks calcium and magnesium. For T25 flasks, use 3-5 ml of PBS, and for T75 flasks, use 5-10 ml. Then, cover the cells completely with Accutase, using 1-2 ml for T25 flasks and 2.5 ml for T75 flasks. Let the cells incubate at room temperature for 8-10 minutes to detach them. After incubation, gently mix the cells with 10 ml of medium to resuspend them, then centrifuge at 300xg for 3 minutes. Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells in fresh medium, and transfer them into new flasks that already contain fresh medium. |
| Split ratio | 1:2 to 1:4 |
| Fluid renewal | 2 to 3 times per week |
| Freeze medium | CM-1 (Cytion catalog number 800100) or CM-ACF (Cytion catalog number 806100) |
| Handling of cryopreserved cultures |
|
Quality control / Genetic profile / HLA
| Sterility | Mycoplasma contamination is excluded using both PCR-based assays and luminescence-based mycoplasma detection methods. To ensure there is no bacterial, fungal, or yeast contamination, cell cultures are subjected to daily visual inspections. |
|---|---|
| STR profile |
Amelogenin: x,x
CSF1PO: 8,10
D13S317: 8,11
D16S539: 12,13
D5S818: 11,13
D7S820: 8,10
TH01: 6,10
TPOX: 11
vWA: 15,16,17,22
D3S1358: 16,19
D21S11: 27,29,30
D18S51: 11,12
Penta E: 11,13
Penta D: 10,11
D8S1179: 9,13,14
FGA: 20,21,22,23
D1S1656: 14,17.3
D6S1043: 14,19
D2S1338: 16
D12S391: 15,19,20
D19S433: 14
|
