MCF-7 Cells









Essential facts about the MCF7 breast cancer cell line
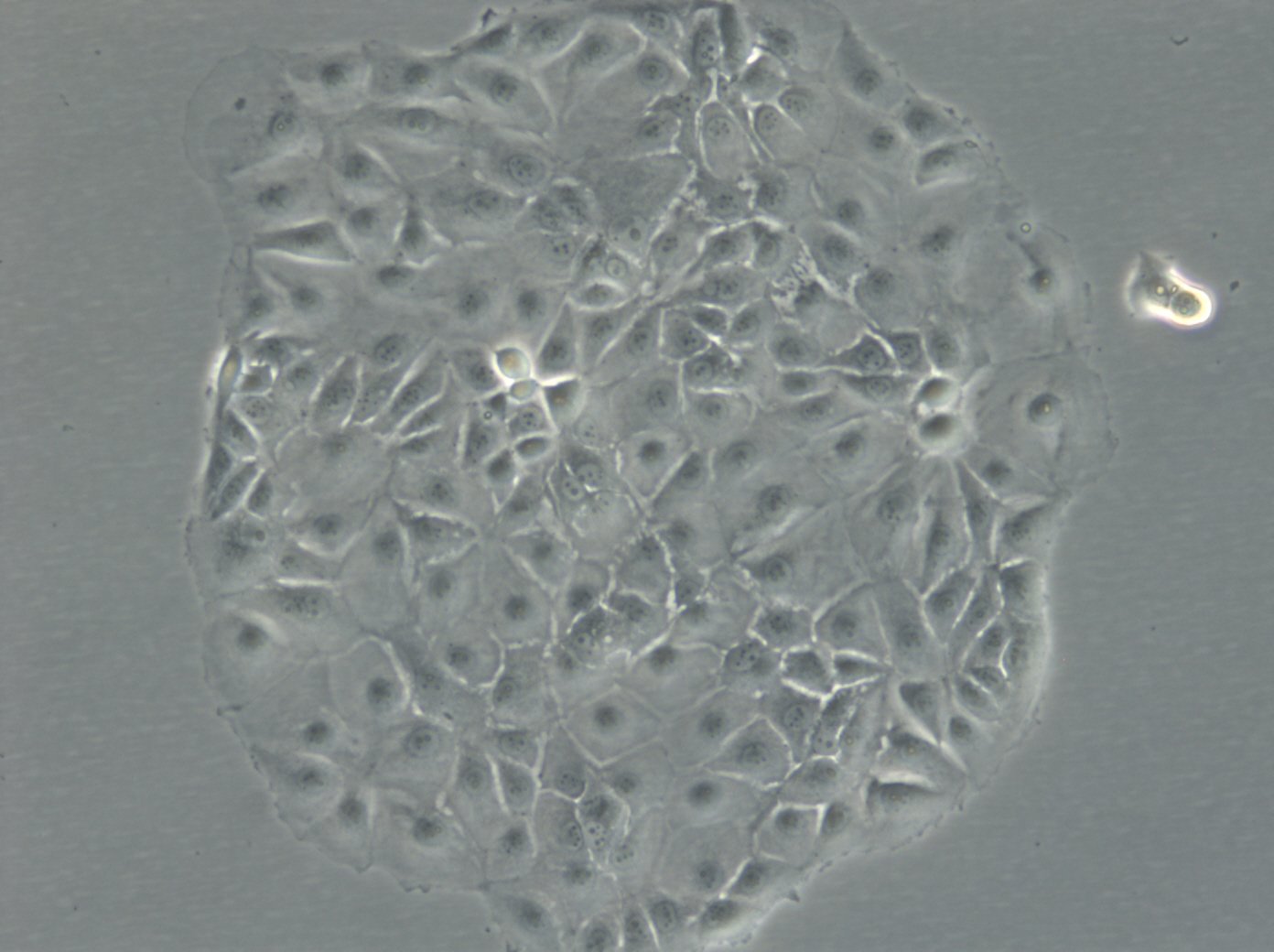
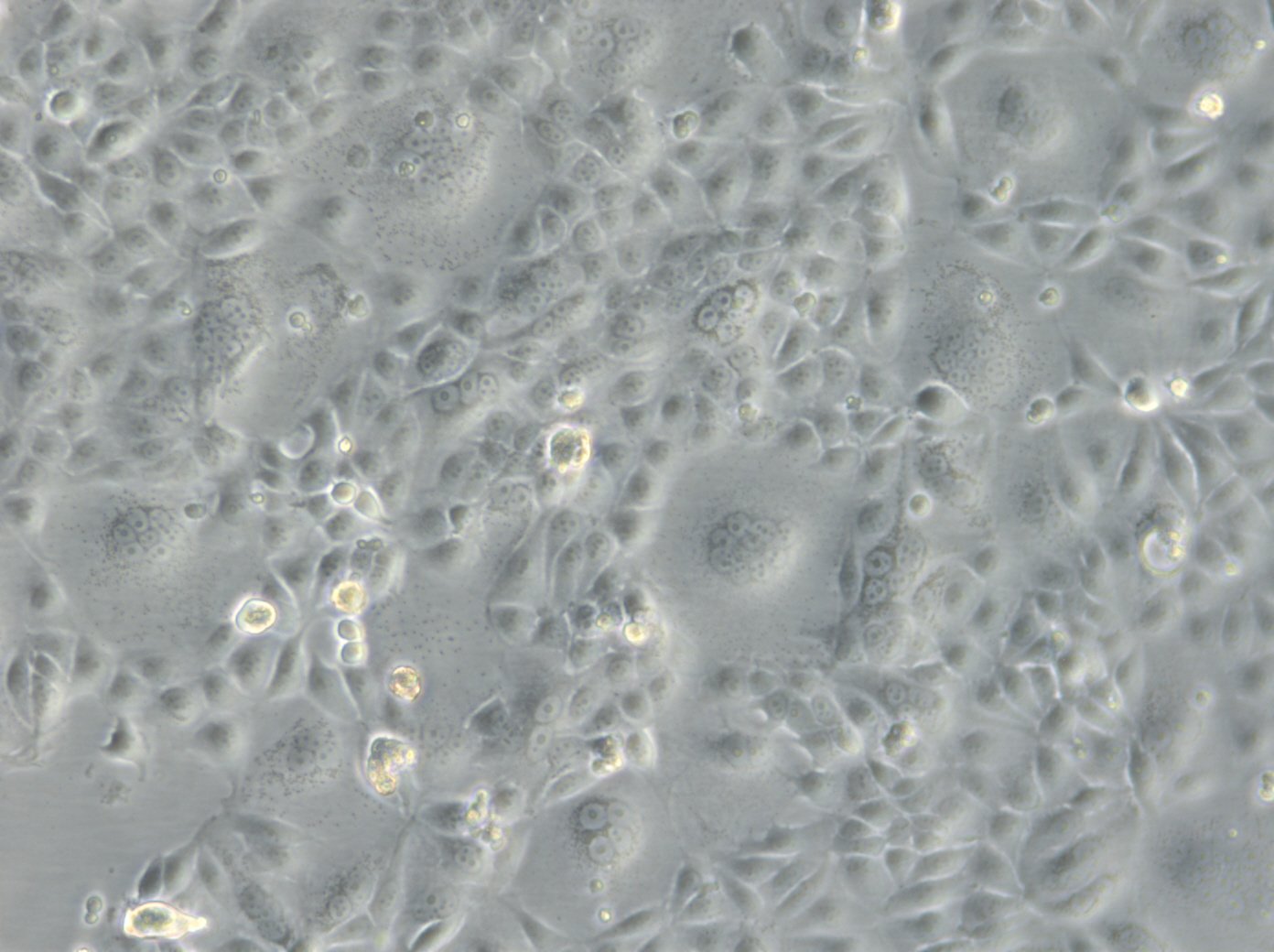
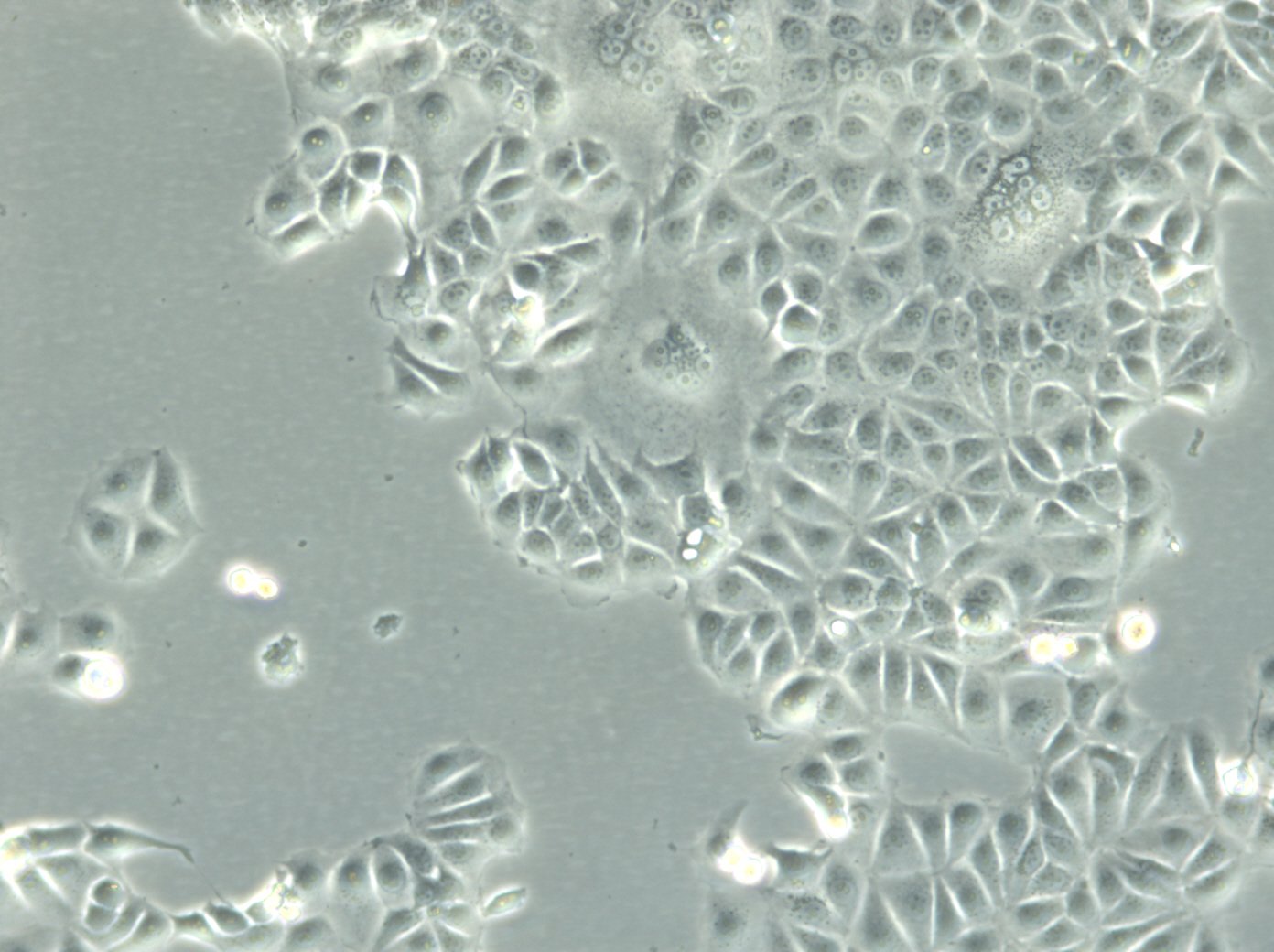
| Description | MCF7 cells, a widely used research model in human breast cancer research, are utilized extensively as an in vitro model for hormone-dependent breast cancer. Originating from the breast tissue of a 69-year-old white female with metastatic adenocarcinoma, MCF7 cells are a widely used in vitro model for hormone-dependent breast cancer, reflecting the Luminal A subtype. This subtype is characterized by a lower grade and better prognosis compared to more aggressive forms of breast cancer. In the realm of breast cancer research, MCF 7 cells are instrumental in evaluating the efficacy of breast cancer drugs and understanding the dynamics of breast cancer stem cells. They are central to cancer research, serving as a comparative model against more aggressive cell lines like MDA-MB-231. The investigation of therapeutic agents, such as tamoxifen and doxorubicin, is critical in drug discovery efforts targeting hormone-dependent breast cancers and gaining insights into the mechanisms of action and resistance. Similarly, the role of estradiol in modulating the growth and characteristics of these cells is a subject of significant interest, given its relevance to hormone-responsive breast cancers. Research employing the MCF7 breast cancer cell line often delves into the cellular processes of cytotoxicity and apoptosis, especially in response to cancer agents like curcumin, known for its potential in cancer prevention. The study of immune responses, including the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and the impact of bacterial antigens, further enriches our understanding of the tumor microenvironment and potential therapeutic targets. MCF7 cells are meticulously studied in both 2D cell culture and 3D cell culture systems, including spheroid culture, to mimic tumor microenvironments more closely. These methodologies enable a more profound exploration of cell spheroid growth and the behavior of cancer stem cells within microtissues in scaffold-based systems. The MCF7 cell line, with its epithelial cell characteristics and resemblance to human adenocarcinoma cells, is a cornerstone of cancer research. It facilitates not only the exploration of breast cancer drugs and their mechanisms but also the broader implications for cancer treatment, including the potential role of mesenchymal stem cells and the efficacy of targeted therapies in vivo studies. |
|---|---|
| Organism | Human |
| Tissue | Breast |
| Disease | Adenocarcinoma |
| Metastatic site | Pleural effusion |
| Synonyms | MCF 7, MCF.7, MCF7, Michigan Cancer Foundation-7, ssMCF-7, ssMCF7, MCF7/WT, MCF7-CTRL, IBMF-7 |
Features
| Age | 69 years |
|---|---|
| Gender | Female |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian |
| Morphology | Epithelial-like |
| Growth properties | Monolayer, adherent |
Documentation
| Citation | MCF-7 (Cytion catalog number 300273) |
|---|---|
| Biosafety level | 1 |
Genetic profile
| Receptors expressed | The cells express the wildtype and variant estrogen receptors as well as progesterone receptor. |
|---|---|
| Protein expression | p53 negative, pGP9.5 negative, CEA positive |
| Isoenzymes | PGM3, 1, PGM1, 1-2, ES-D, 1-2, AK-1, 1, GLO-1, 1-2, G6PD, B, |
| Oncogenes | wnt7h +, Tx-4 |
| Tumorigenic | Yes, in nude mice |
| Products | Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP) BP-2, BP-4, BP-5 |
| Mutational profile | TP53 wt |
| Karyotype | The stemline chromosome numbers ranged from hypertriploidy to hypotetraploidy, with the 2S component occurring at 1%. There were 29 to 34 marker chromosomes per S metaphase, 24 to 28 markers occurred in at least 30% of cells, and generally one large submetacentric (M1) and 3 large subtelocentric (M2, M3, and M4) markers were recognizable in over 80% of metaphases. No DM were detected. Chromosome 20 was nullisomic and x was disomic. Phenotype Frequency Product: 0.0154 |
MCF7 cell culturing methods
| Culture Medium | EMEM, w: 2 mM L-Glutamine, w: 1.5 g/L NaHCO3, w: EBSS, w: 1 mM Sodium pyruvate, w: NEAA (Cytion article number 820100c) |
|---|---|
| Medium supplements | Supplement the medium with 10% FBS |
| Passaging solution | Accutase |
| Doubling time | 24 hours |
| Subculturing | Remove the old medium from the adherent cells and wash them with PBS that lacks calcium and magnesium. For T25 flasks, use 3-5 ml of PBS, and for T75 flasks, use 5-10 ml. Then, cover the cells completely with Accutase, using 1-2 ml for T25 flasks and 2.5 ml for T75 flasks. Let the cells incubate at room temperature for 8-10 minutes to detach them. After incubation, gently mix the cells with 10 ml of medium to resuspend them, then centrifuge at 300xg for 3 minutes. Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells in fresh medium, and transfer them into new flasks that already contain fresh medium. |
| Split ratio | A ratio of 1:3 to 1:6 is recommended |
| Seeding density | 3 x 10^4 cells/cm^2 |
| Fluid renewal | 2 to 3 times per week |
| Freezing recovery | Allow the cells to rest for 48 hours past thawing |
| Freeze medium | CM-1 (Cytion catalog number 800100) or CM-ACF (Cytion catalog number 806100) |
| Handling of cryopreserved cultures |
|
Quality control
| Sterility | Mycoplasma contamination is excluded using both PCR-based assays and luminescence-based mycoplasma detection methods. To ensure there is no bacterial, fungal, or yeast contamination, cell cultures are subjected to daily visual inspections. |
|---|---|
| STR profile |
CSF1PO: 10
D13S317: 11
D16S539: 11,12
D5S818: 12
D7S820: 8,9
TH01: 6
TPOX: 9,12
vWA: 14,15
D3S1358: 16
D21S11: 30
D18S51: 14
Penta E: 7,12
Penta D: 12
D8S1179: 10,14
FGA: 23,25
D1S1656: 15.3
D6S1043: 12,18
D2S1338: 21,23
D12S391: 18,20
D19S433: 13,14
|
| HLA alleles |
A*: 02:01:01
B*: 18:01:01, 44:02:01
C*: 05:xx
DRB1*: 03:01:01, 15:01:01
DQA1*: 01:02:01, 05:01:01
DQB1*: 02:01:01, 06:02:01
DPB1*: 02:01:02, 04:01:01
E: 01:01:01
|
Required products
In biological research, the cryopreservation of mammalian cells is an invaluable tool. Successful preservation of cells is a top priority given that losing a cell line to contamination or improper storage conditions leads to lost time and money, ultimately delaying research results. Once the cells have been transferred from a cell growth medium to a freezing medium, the cells are typically frozen at a regulated rate and stored in liquid nitrogen vapor or at below -130°C in a mechanical deep freezer. The freeze medium CM-ACF enables cryopreservation of cells at below -130°C (or in liquid nitrogen), essentially eliminating the need for an additional, costly ultralow freezer and eliminating time-consuming and demanding controlled rate freezing processes. Simply collect the cells, aspirate the growth medium, resuspend in CM-ACF, transfer to a cryovial, and store the vial at below -130 °C.
Long shelf-life
CM-ACF is a serum-free, ready-to-use cryopreservation medium that can be stored in the refrigerator for up to one year.
Trusted by hundreds of researchers
Our advanced, serum-free cell freezing medium CM-ACF is a market-leading product in Germany and Europe and is distinguished by numerous publications involving hundreds of different cell lines worldwide. We tested it with more than 1000 cell lines from our proprietary cell bank.
Optimized serum-free ingredients
CM-ACF does not contain serum products. Serum-containing cryopreservation mediums have the disadvantage of fluctuating recovery rates and unclear composition. Since the composition and concentration of proteins and other biological components vary from batch to batch in serum, the reproducibility of experiments with cells that were frozen in a serum-containing medium may be compromised. As each component of CM-ACF is carefully defined, you can rest assured that cells always recover identically.
Contains DMSO, glucose, salts
Buffering capacity pH = 7.2 to 7.6
Universal
- even for stem cell preservation
All common cell lines can be frozen and thawed to yield many viable cells. Compared to standard media, the rate of recovery of even the most delicate cells is significantly higher. Using CM-ACF, we store over 1000 different cell lines with outstanding success.
Applications & Validation
The cells preserved in our CM-ACF freeze medium can be used for cell counting, viability and cryopreservation, cell culture, mammalian cell culture, gene expression analysis and genotyping, in vitro transcription, and polymerase chain reactions. Each batch's efficacy is evaluated using CHO-K1 cells. Each batch is tested for pH, osmolality, sterility, and endotoxins to ensure high quality.
In biological research, the cryopreservation of mammalian cells is an invaluable tool. Successful preservation of cells is a top priority given that losing a cell line to contamination or improper storage conditions leads to lost time and money, ultimately delaying research results. Once the cells have been transferred from a cell growth medium to a freezing medium, the cells are typically frozen at a regulated rate and stored in liquid nitrogen vapor or at below -130°C in a mechanical deep freezer. The freeze medium CM-1 enables cryopreservation of cells at below -130°C (or in liquid nitrogen), essentially eliminating the need for an additional, costly ultralow freezer and eliminating time-consuming and demanding controlled rate freezing processes. Simply collect the cells, aspirate the growth medium, resuspend in CM-1, transfer to a cryovial, and store the vial at below -130 °C.
Long shelf-life
CM-1 is a serum-containing, ready-to-use cryopreservation medium that can be stored in the refrigerator for up to one year.
Trusted by hundreds of researchers
Our advanced cell freezing medium CM-1 is a market-leading product in Germany and Europe and is distinguished by numerous publications involving hundreds of different cell lines worldwide. We tested it with more than 1000 cell lines from our proprietary cell bank.
Optimized ingredients
CM-1 does contain serum products. Serum-containing cryopreservation mediums optimally protect the cells whilst being frozen and have the advantage of high recovery rates. As CM-1 has been tested with a multitude of cell lines, you can rest assured that your cells always recover well.
Contains FBS, DMSO, glucose, salts
Buffering capacity pH = 7.2 to 7.6
Applications & Validation
The cells preserved in our CM-1 freeze medium can be used for cell counting, viability and cryopreservation, cell culture, mammalian cell culture, gene expression analysis and genotyping, in vitro transcription, and polymerase chain reactions. Each batch's efficacy is evaluated using CHO-K1 cells. Each batch is tested for pH, osmolality, sterility, and endotoxins to ensure high quality.
This EMEM medium consists of 2 mM L-Glutamine, 1.5 g/L NaHCO3, EBSS, 1 mM Sodium pyruvate, and NEAA.
What's in EMEM?
EMEM is a modified version of Eagle's minimum essential medium, containing Earle's Balanced Salt Solution, non-essential amino acids, L-glutamine, sodium pyruvate, and sodium bicarbonate. It's important to note that this reduced level of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3, 1.5 g/L) is intended for use in 5% CO2 in the air. To maintain its effectiveness, storing the medium at two °C to 8°C in the dark when not in use is recommended.
What is EMEM used for?
Eagle's minimal essential medium (EMEM) is a cell culture medium that can maintain cells in tissue culture. The medium contains higher concentrations of amino acids, allowing for a more accurate approximation of the protein composition of cultured mammalian cells. EMEM may be used to cultivate various cells, including fibroblasts, human liver cancer cell line (HepG2) cells and human fetal brain progenitor-derived astrocyte cells (PDA). It is typically used in the presence of fetal bovine serum (FBS), calf, or horse sera.
How is EMEM different from other cell culture media?
While EMEM and Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) share some similarities, they also differ. Both media lack protein and contain the amino acids, salts, glucose, and vitamins required to provide a cell with energy and maintain it in tissue culture. However, the DMEM formulation is modified to contain up to four times more vitamins and amino acids and two to four times more glucose than EMEM. It's worth noting that EMEM is also different from the original MEM formulation.
Quality control
pH = 7.2 +/
- 0.02 at 20-25°C.
Each lot has been tested for sterility and absence of mycoplasma and bacteria.
Maintenance
Keep refrigerated at +2°C to +8°C in the dark. Freezing and warming up to +37° C minimize the quality of the product.
Do not heat the medium to more than 37° C or use uncontrollable sources of heat (e.g., microwave appliances).
If only a part of the medium is to be used, remove this amount from the bottle and warm it up at room temperature.
Shelf life for any medium except for the basic medium is 8 weeks from the date of manufacture.
Composition
Components
mg/L
Inorganic Salts
Calcium chloride x 2H2O
264,92
Magnesium sulfate
97,67
Potassium chloride
400,00
Sodium chloride
6,800.00
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate x H2O
140,00
Other Components
D(+)-Glucose
1,000.00
Phenol red
10,00
Sodium pyruvate
110,00
NaHCO3
1,500.00
Amino Acids
L-Alanine
8,90
L-Arginine x HCl
126,00
L-Asparagine x H2O
13,20
L-Aspartic acid
13,30
L-Cystine
24,00
L-Glutamine
292,30
L-Glutamic acid
14,70
Glycine
7,50
L-Histidine x HCl x H2O
42,00
L-Isoleucine
52,00
L-Leucine
52,00
L-Lysine x HCl
72,50
L-Methionine
15,00
L-Phenylalanine
32,00
L-Proline
11,50
L-Serine
10,50
L-Threonine
48,00
L-Tryptophan
10,00
L-Tyrosine
36,00
L-Valine
46,00
Vitamins
D-Calcium pantothenate
1,00
Choline chloride
1,00
Folic acid
1,00
myo-Inositol
2,00
Nicotinamide
1,00
Pyridoxal x HCl
1,00
Riboflavin
0,10
Thiamine x HCl
1,00
- A Gentle Alternative to Trypsin
Accutase is a cell detachment solution that is revolutionizing the cell culture industry. It is a mix of proteolytic and collagenolytic enzymes that mimics the action of trypsin and collagenase. Unlike trypsin, Accutase does not contain any mammalian or bacterial components and is much gentler on cells, making it an ideal solution for the routine detachment of cells from standard tissue culture plasticware and adhesion coated plasticware. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and uses of Accutase and how it is changing the game in cell culture.
Advantages of Accutase
Accutase has several advantages over traditional trypsin solutions. Firstly, it can be used whenever gentle and efficient detachment of any adherent cell line is needed, making it a direct replacement for trypsin. Secondly, Accutase works extremely well on embryonic and neuronal stem cells, and it has been shown to maintain the viability of these cells after passaging. Thirdly, Accutase preserves most epitopes for subsequent flow cytometry analysis, making it ideal for cell surface marker analysis.
Additionally, Accutase does not need to be neutralized when passaging adherent cells. The addition of more media after the cells are split dilutes Accutase so it is no longer able to detach cells. This eliminates the need for an inactivation step and saves time for cell culture technicians. Finally, Accutase does not need to be aliquoted, and a bottle is stable in the refrigerator for 2 months.
Applications of Accutase
Accutase is a direct replacement for trypsin solution and can be used for the passaging of cell lines. Additionally, Accutase performs well when detaching cells for the analysis of many cell surface markers using flow cytometry and for cell sorting. Other downstream applications of Accutase treatment include analysis of cell surface markers, virus growth assay, cell proliferation, tumor cell migration assays, routine cell passage, production scale-up (bioreactor), and flow cytometry.
Composition of Accutase
Accutase contains no mammalian or bacterial components and is a natural enzyme mixture with proteolytic and collagenolytic enzyme activity. It is formulated at a much lower concentration than trypsin and collagenase, making it less toxic and gentler, but just as effective.
Efficiency of Accutase
Accutase has been shown to be efficient in detaching primary and stem cells and maintaining high cell viability compared to animal origin enzymes such as trypsin. 100% of cells are recovered after 10 minutes, and there is no harm in leaving cells in Accutase for up to 45 minutes, thanks to autodigestion of Accutase.
In summary
In conclusion, Accutase is a powerful solution that is changing the game in cell culture. With its gentle nature, efficiency, and versatility, Accutase is the ideal alternative to trypsin. If you are looking for a reliable and efficient solution for cell detachment, Accutase is the solution for you.
Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) is a versatile buffer solution used in many biological and chemical applications, as well as tissue processing. Our PBS solution is formulated with high-quality ingredients to ensure a constant pH during experiments. The osmolarity and ion concentrations of our PBS solution are matched to those of the human body, making it isotonic and non-toxic to most cells.
Composition of our PBS Solution
Our PBS solution is a pH-adjusted blend of ultrapure-grade phosphate buffers and saline solutions. At a 1X working concentration, it contains 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8 mM Na2HPO4, and 2 mM KH2PO4. We have chosen this composition based on CSHL protocols and Molecular cloning by Sambrook, which are well-established standards in the research community.
Applications of our PBS Solution
Our PBS solution is ideal for a wide range of applications in biological research. Its isotonic and non-toxic properties make it perfect for substance dilution and cell container rinsing. Our PBS solution with EDTA can also be used to disengage attached and clumped cells. However, it is important to note that divalent metals such as zinc cannot be added to PBS as this may result in precipitation. In such cases, Good's buffers are recommended. Moreover, our PBS solution has been shown to be an acceptable alternative to viral transport medium for the transport and storage of RNA viruses, such as SARS-CoV-2.
Storage of our PBS Solution
Our PBS solution can be stored at room temperature, making it easy to use and access.
To sum up
In summary, our PBS solution is an essential component in many biological and chemical experiments. Its isotonic and non-toxic properties make it suitable for numerous applications, from cell culture to viral transport medium. By choosing our high-quality PBS solution, researchers can optimize their experiments and ensure accurate and reliable results.
Composition
Components
mg/L
Inorganic Salts
Potassium chloride
200,00
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
200,00
Sodium chloride
8,000.00
di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous
1,150.00