HuCC-T1 Cells
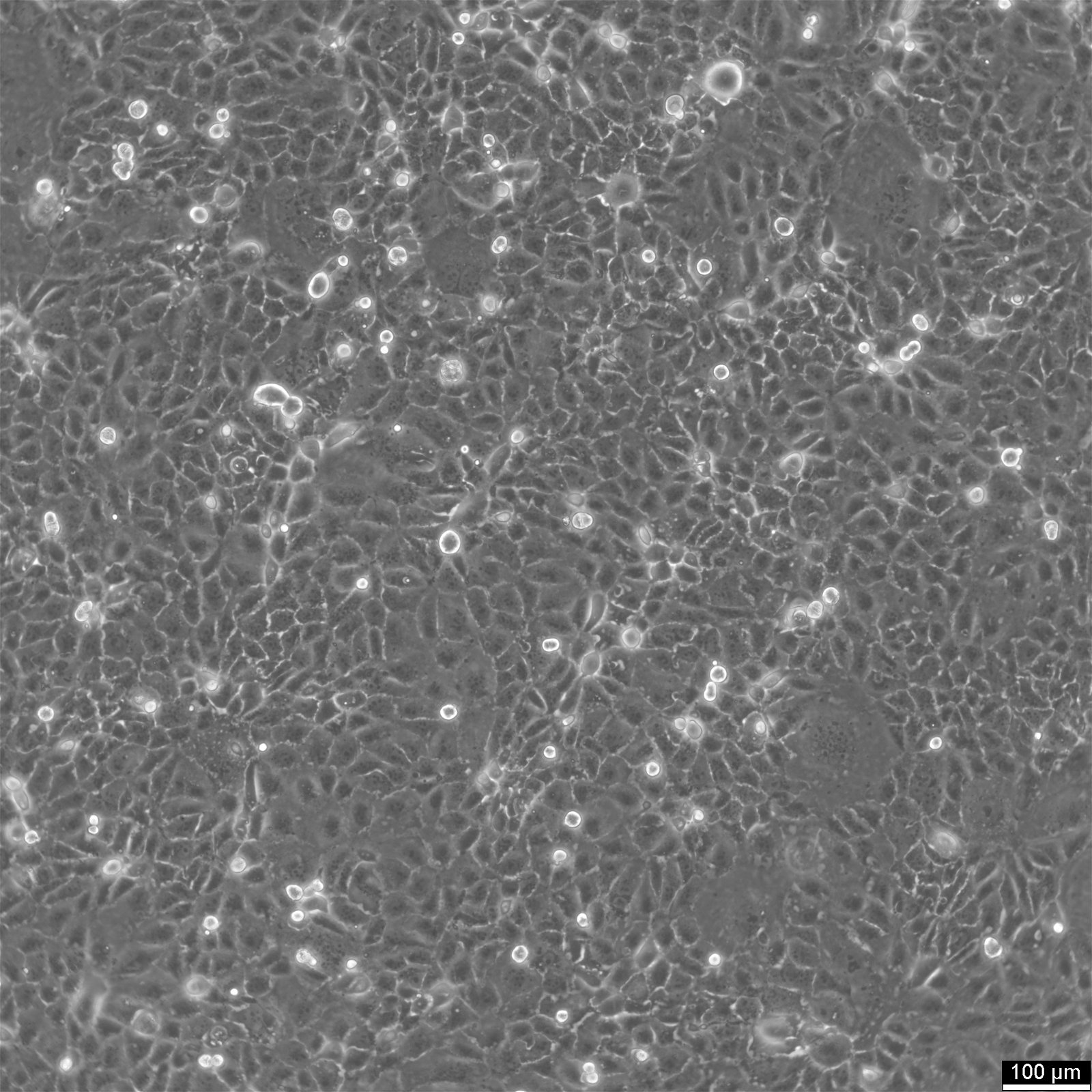
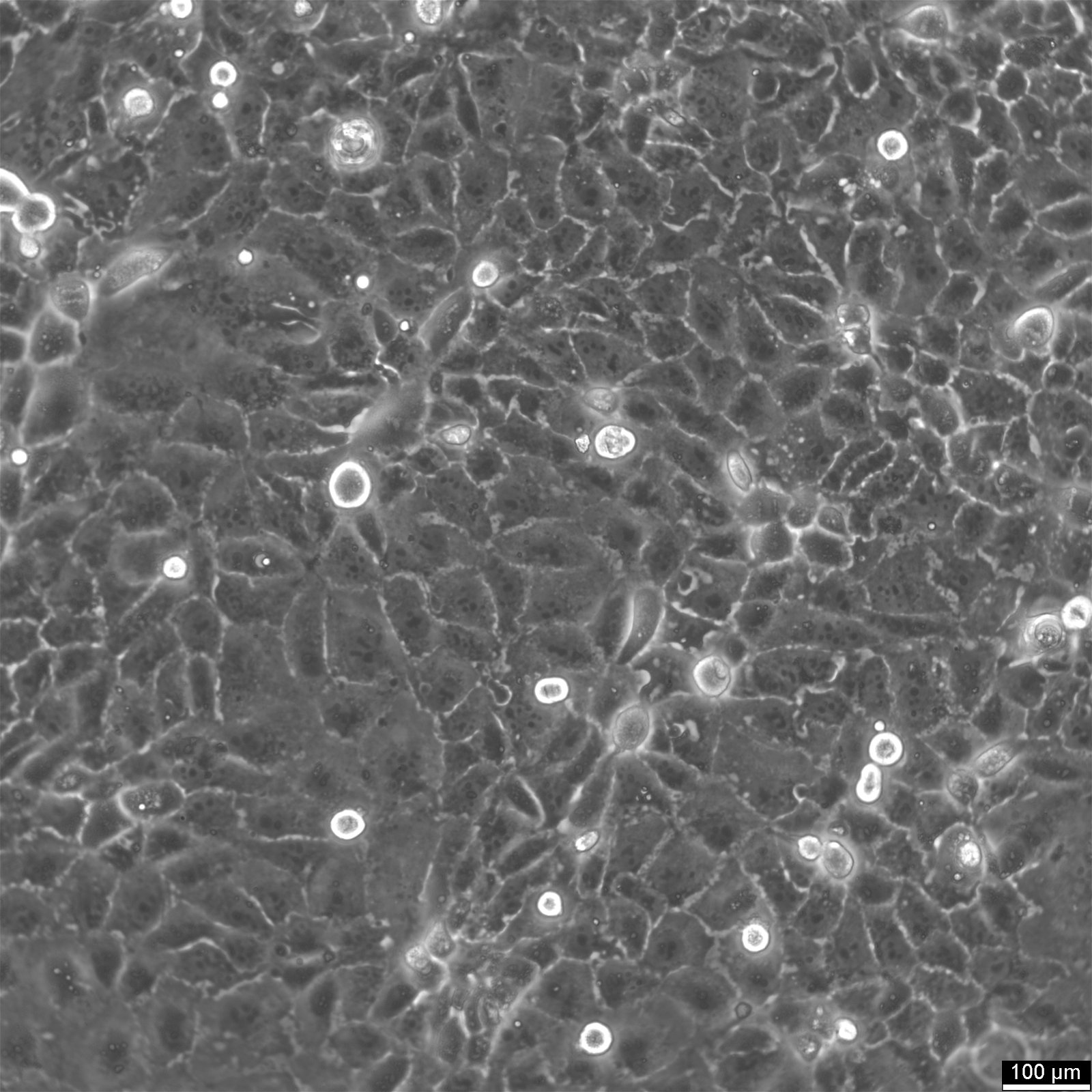






General information
| Organism | Human |
|---|---|
| Tissue | Liver |
| Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma |
| Metastatic site | Ascites |
| Applications | Studies of the mechanism of tumor marker secretion and tumor cell growth in the human cholangiocellular carcinoma |
| Synonyms | HuCCT-1, HUCCT-1, HUCC-T1, HUCCT1, HuCCT1 |
Characteristics
| Age | 56 years |
|---|---|
| Gender | Male |
| Ethnicity | Japanese |
| Morphology | Epithelial |
| Growth properties | Adherent |
Identifiers / Biosafety / Citation
| Citation | HuCC-T1 (Cytion catalog number 300469) |
|---|---|
| Biosafety level | 1 |
Expression / Mutation
| Tumorigenic | Yes, in nude mice. |
|---|
Handling
| Culture Medium | RPMI 1640, w: 2.1 mM stable Glutamine, w: 2.0 g/L NaHCO3 (Cytion article number 820700a) |
|---|---|
| Medium supplements | Supplement the medium with 10% FBS |
| Passaging solution | Trypsin-EDTA |
| Subculturing | Discard the old medium and wash the cells with PBS. Add a freshly prepared 0.025% trypsin/0.02% EDTA solution heated to 37 degrees Celsius and wait until the cells detach, which usually takes about 5 minutes. Neutralize the trypsin by adding fresh medium, then transfer the cell mixture to a tube and centrifuge. After centrifugation, remove the supernatant, resuspend the cell pellet in fresh culture medium, and transfer the suspension to new flasks. Incorporate G418 into the culture medium to achieve a final concentration of 0.5 mg/ml |
| Freeze medium | CM-1 (Cytion catalog number 800100) or CM-ACF (Cytion catalog number 806100) |
| Handling of cryopreserved cultures |
|
Quality control / Genetic profile / HLA
| Sterility | Mycoplasma contamination is excluded using both PCR-based assays and luminescence-based mycoplasma detection methods. To ensure there is no bacterial, fungal, or yeast contamination, cell cultures are subjected to daily visual inspections. |
|---|---|
| STR profile |
Amelogenin: x,y
CSF1PO: 11,12
D13S317: 11,13
D16S539: 11,12
D5S818: 12,13
D7S820: 10,11
TH01: 7,10
TPOX: 8
vWA: 18
D3S1358: 15
D21S11: 31
D18S51: 13
Penta E: 15,18
Penta D: 10
D8S1179: 10
FGA: 20,23
D6S1043: 13
D2S1338: 17,18
D12S391: 18,20
D19S433: 13
|
